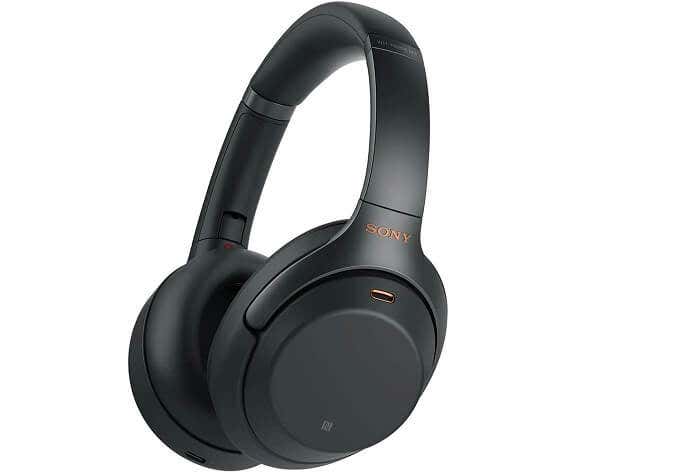
So you can make an informed choice when buying
Noise. It’s all around us. Whether it’s a crying baby, the hum of an air conditioner or the animated babble of your office co-workers. A quiet place to work or enjoy some relaxation is becoming a truly premium commodity. Noise cancellation technology can help bring the zen back into your life.
The question is, how does noise cancellation work? Let’s go over the principles of the technology, so you can make an informed choice when buying your own noise-cancelling equipment.

A (Very) Basic Overview of Sound
Sound is energy travelling as a wave through some form of matter. We generally hear sound transmitted through the air.
For example, a guitar string vibrates in air, knocking air molecules about. Those molecules knock into their neighbors, and so on. When the wave moving through the air hits your ear drums, it moves them at the same frequency as the guitar string.
Your brain converts that movement into electrical signals that you then perceive as sound. That’s a very simplistic explanation of what sound is, but it’s the least you need to know to understand noise cancellation.
A (Very) Basic Overview of Anti-sound
A wave has different properties. It has a frequency, which is how often the wave goes through a full cycle.
Using our guitar string as an example again. The frequency is how quickly the string moves through one full vibration. We perceive higher frequency sound as high-pitched. Lower frequency sound is more bassy. Apart from frequency, waves also have amplitude. That’s the height of the wave’s peak. Next, the wave also has a phase. This is the position of the peaks and troughs of the wave.
If you generate a sound wave that has the same amplitude, but the opposite phase (the peaks are where the troughs of the other wave are), it causes destructive interference. The two waves essentially cancel each other out. This can be done at large scale, where you need to have just as much energy in your anti-noise generator as the original sound itself. However, if you only want to cancel noise for one person, you don’t need much power at all, which is where noise cancelling headphones come in.
Noise Cancelling Headphones
Noise cancelling headphones are technological marvels. On the outside of the headphones, there are microphones that sample the ambient noise outside the headphones. This sound is analyzed by onboard electronics, using a mathematical algorithm. Each headphone maker has its own secret-sauce algorithm, which all work to differing levels of effectiveness.
The algorithm is used to calculate the anti-noise wave needed to destructively interfere with the ambient noise where you are. Then a device known as a transducer, which is essentially a type of speaker, generates the anti-noise wave.
The end effect is that when you switch on the noise cancellation function, you’re suddenly enveloped in (near) silence. Which allows you to enjoy your audio at much better fidelity or just enjoy some peace and quiet.
Active and Passive Noise Cancellation
The process we just described is usually referred to on product specification sheets as “active noise cancellation” or something similar. Confusingly, some headphones claim to have something called “passive” noise cancellation.
It’s very important not to confuse these two features. There really isn’t such a thing as passive noise cancellation. What this term actually means is that a given pair of headphones were designed to block out sound using plain old soundproofing.

This means that the materials and design of the headphones isolate you from outside noise to some extent. From that point of view, sticking your fingers in your ears is also “passive noise cancellation”.
There’s much to be said for a pair of headphones that offer great sound isolation, but linking that to noise cancellation is a bit of marketing sleight of hand.
The Limitations of Active Noise Cancellation

Current active noise cancellation technology can’t block out noise perfectly. They work incredibly well when it comes to constant, predictable sources of noise. Think of a jet engine, the hum of an air conditioner or your fridge compressor. Modern active noise cancellation is incredibly good at erasing that type of sound completely.
Conversely, sudden unpredictable sounds pose much more of a challenge. This usually includes loud human conversations, someone breaking a glass cup or any other noise that the algorithm doesn’t have time to analyze. That being said, new cutting edge systems with faster processors and more sophisticated algorithms are beginning to deal with these types of noise as well.
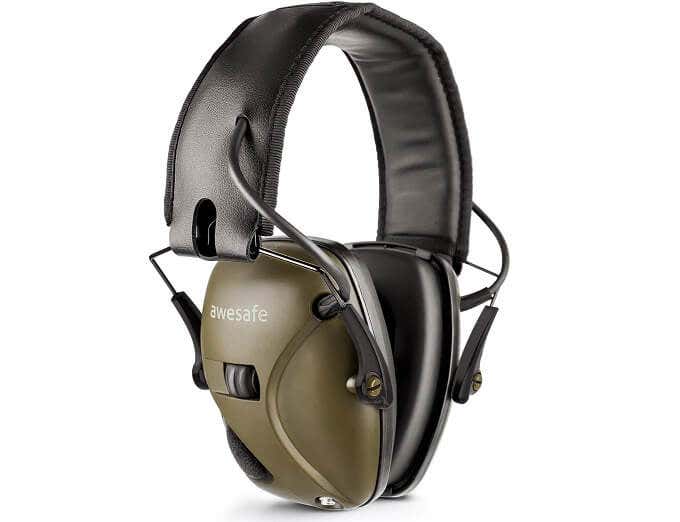

One interesting example of such specialized active noise cancellation technology comes in the form of electronic earmuffs used when firing rifles, pistols and other firearms.
These earmuffs use passive sound isolation to block out all sound, just as regular shooting earmuffs do. However, they have external microphones that pass through sound around you, to maintain situational awareness. So you can have a conversation with another person with ease. However, the maximum volume of all sound around you is kept under a comfortable maximum.
These systems can often provide directional sound and amplify quiet sounds as well, while cancelling out gunshots. It’s not exactly the same technology as mainstream noise cancellation headphones, but it’s closely related.
AI-Powered Noise Removal

A fairly new development is the application of artificial intelligence technology to remove unwanted noise from an audio signal. Unfortunately this can’t quite happen in real time just yet, so it isn’t effective at noise cancellation. What it is very good at is removing noise from a microphone signal.
For example, if you’re trying to Skype someone or make a voice recording in a noisy environment, it can be hard for the person on the other end to understand what you’re saying. Using artificial intelligence, that audio stream can be analyzed and everything but your own voice can be removed.
For example, Nvidia’s RTX Voice application uses the special deep learning hardware in their RTX graphics cards to process microphone audio. So whether someone is typing on a keyboard, vacuuming the floor, or doing construction work, none of that will be audible to your audience. You can see a demonstration of this incredible technology here.
Since there’s enough time between where you speak into the microphone and the other person hears the audio for the AI to do it’s work, there’s no issue in terms of real time limitations. Perhaps with technological advancement these super-effective AI noise removal methods will work as a form of headphone noise cancellation as well.
Noise Cancelling Microphones
Moving on from headphones, another place where a similar technology can be very useful for most people, especially now that so many of us rely on remote work, are noise-cancelling microphones.
Once again, even though the marketing language uses the term “noise-cancelling”, these microphones don’t generate anti-noise to interfere with the source of the noise. Instead, they take the sound as a whole and then apply the same sort of noise-identifying algorithm to it. Removing it from the input audio stream before passing it on.
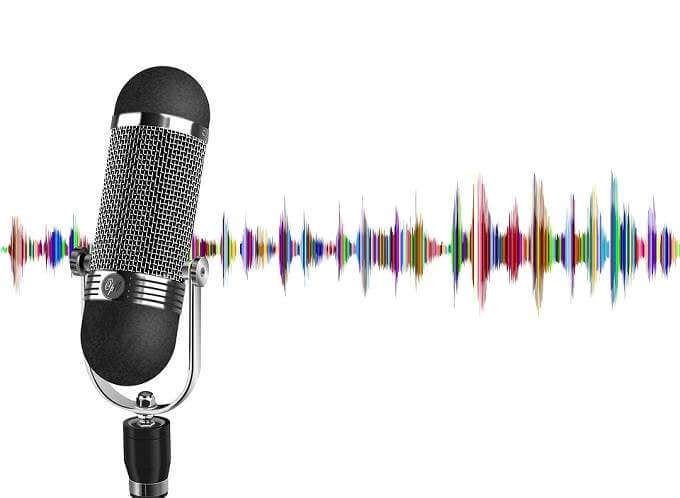

You even get in-line AI-powered microphone noise removal solutions, such as this ASUS adapter. Plug it into a USB port, connect your headset to it and the little electronic brain inside will remove unwanted noises, leaving only your crystal clear voice behind.
The Sound of Silence
You don’t really notice how much the constant noise of modern life grinds you down until you manage to block it out. Slipping on a pair of good noise-cancelling headphones can feel like a refreshing wind blowing away your low-level anxiety.
Now that you know how noise cancellation works, you can make more informed decisions about your anti-noise kit of choice. If you buy the right stuff, you’ll find that the sound of silence really is the best music you can get.